
Video
How to Lose Fat and STAY LEAN as an AthleteWeight management for athletes -
Written by SCAN Registered Dietitians RDs. For advice on customizing a nutrition plan for weight management, consult a RD who specializes in sports, particularly a Board Certified Specialist in Sports Dietetics CSSD. Find a SCAN RD at www.
Sports, Cardiovascular, and Wellness Nutrition Dietetic Practice Group, Rosenbloom C, Coleman E. Sports Nutrition: A Practice Manual for Professionals, 5th edition.
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: The use of software that blocks ads hinders our ability to serve you the content you came here to enjoy. We ask that you consider turning off your ad blocker so we can deliver you the best experience possible while you are here. The following are some guidelines to consider: Weight Loss Weight loss for athletes is a balancing act focusing on eating enough to support training and performance while creating an energy deficit to lose weight.
Therefore, it is best to focus on weight loss during the off season or rest phase of the training cycle. Athletes who are trying to decrease body fat may consume protein at a level of 1. Build a balanced diet focused on nutrient-dense foods such as lean proteins, beans and legumes, low-fat dairy, fruit, vegetables, and whole grains.
Do not skip meals. Instead, reduce portion sizes. Weight Gain Gains in muscle mass will best be achieved when in positive energy balance. Muscles take time to grow so it is important to set realistic goals.
Focus first on consuming adequate carbohydrates. Proper refueling is especially important for days with two training sessions or when you have fewer than eight hours of recovery time between workouts and events 2.
Athletes following carb-restricted diets should aim to consume between 0. Adding 20—25 grams of protein can further speed up recovery and promote protein production in your muscles 2.
SUMMARY Consuming a good amount of carbs and protein immediately after training can help maintain your sports performance during weight loss. Individuals attempting to lose weight are often at risk of losing some muscle in addition to fat.
Athletes are no exception. Some muscle loss can be prevented by eating a sufficient amount of protein, avoiding crash diets, and lifting weights 3. Research shows that both protein intake and strength-training exercises stimulate muscle protein synthesis.
Nevertheless, make sure to speak to your coach before adding any extra workouts to your schedule. This will reduce your risk of overtraining or injuries. SUMMARY Strength-training exercises can help prevent the muscle loss often experienced during a period of weight loss.
Researchers believe these adaptations can persist for some time after you bump up your calorie intake and cause you to quickly regain the lost fat 5.
This may help restore your hormone levels and metabolism better, minimizing the weight regain 5. SUMMARY Increasing your calorie intake gradually after a period of weight loss may help minimize weight regain.
Although weight loss is a widely researched topic, the number of studies performed on athletes is limited. Nevertheless, many of the strategies scientifically proven to help non-athletes lose body fat may also benefit athletes.
Thus, you can try some of the following:. SUMMARY Stress, sleep, hydration, and alcohol all affect weight loss. Eating slowly, controlling portion sizes, and sleeping well can all help you lose weight.
Those who want to reduce their body fat levels should aim to do so during the off-season. Keep in mind that lower body fat is not always better.
Athletes should discuss any weight loss goals or strategies with their coach or sports dietitian. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
The arms are often considered a problem area, leaving many people seeking out ways to lose extra arm fat.
Here are 9 ways to decrease arm fat and…. People tend to make many mistakes when they try to lose weight. Here are 15 common weight loss mistakes to avoid. This article explains whether weight…. This article lists 14 common reasons why you're not losing weight.
Many people stop losing before they reach a weight they are happy with. If you're concerned about how to lose leg fat, here's what you can do to target and tone. From protein to carbs, learn how to boost your workouts by fueling your body the way professional athletes do.
Low-carbohydrate, high-fat diets may help endurance athletes perform better, but team and sprint athletes may see a drop in their performance. Targeting heart rate zones as you exercise is one way to maximize the benefits you get from your workouts.
Learn about your different heart rate zones…. There are several causes of numbness in your toes and feet when you run, ranging from poor-fitting shoes to health conditions like diabetes.
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? Brooke Pengel, MD ; Brooke Pengel, MD. Andrew Peterson, MD Andrew Peterson, MD. Pediatrics 3 : e Connected Content. This article has been reaffirmed: AAP Publications Reaffirmed or Retired. Cite Icon Cite. toolbar search toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest.
View Large. Boxing Crew Horse racing—jockeys Martial arts Weight-class football Wrestling. TABLE 3 Sports That Emphasize a Muscular Physique. Baseball Basketball Bodybuilding Football especially linemen Powerlifting Rugby Track eg, shot-put, discus.
TABLE 4 Unhealthy and Healthy Weight Loss Methods. Healthy Weight Loss. Decreased psychomotor function Decreased reaction time Decreased accuracy Decreased mental endurance Decreased alertness Increased problem-solving time Increased fatigue Increased levels of perceived exertion Temporary learning deficits Mood swings Changes in cognitive state.
TABLE 6 LAW1 and LAW2 Calculations. weeks in season wk. TABLE 7 Unhealthy and Healthy Methods of Weight Gain. Rapid weight gain Gradual weight gain Weight gain resulting in excess body fat Weight gain as muscle mass Use of anabolic compounds Boys gain up to 0.
Get adequate sleep. TABLE 8 Summary of Performance-Enhancing Substances Commonly Used by Athletes With Effects on Performance and Possible Adverse Effects.
Usual Form of Intake. Purported Mechanism of Performance Effect. Data on Performance Effects. Potential Adverse Effects. Creatine Creatine is found in meat and fish. Cooking can degrade some creatine in food. Most concern with impact on kidneys because of nephrotic metabolites methylamine and formaldehyde , and specific recommendation against use for athletes at risk for kidney dysfunction.
Causes water retention. Orally ingested creatine monohydrate supplement Anabolic agents Variety of testosterone derivatives. Schedule III drugs. Oral, injectable, buccal, and transdermal forms. Premature physeal closure with decreased final adult height.
Gynecomastia irreversible. Behavior change hypomania, irritability, aggression. Cholestatic jaundice, liver tumors. Cardiac arrhythmias premature ventricular contractions increased blood pressure. Headaches, irritability, sleep disruption, tremor.
Gastric irritation. Increased core temperature with exertion, particularly in hot environments. Significant toxicity has been associated with ingestion of multiple energy drinks, leading to almost emergency department visits in in the to y age group.
Increased risk of liver disease. Individual amino acids or in combination Arginine and citrulline produce increases in nitric oxide see below for further discussion.
HMB is believed to enhance repair of damaged muscle tissue HMB: meta-analysis of studies on young adults show untrained athletes with 6. Synthesized from arginine via reduction to nitrate. Citrulline is an arginine precursor Any potential benefit of arginine appears minimal in healthy young athletes who ingest sufficient protein.
Inorganic forms of nitrate are associated with carcinogenesis, however, current data does not support restriction of vegetable source of nitrates. Carnosine and β-alanine Buffers the metabolic acidosis resulting from high-intensity physical activity.
β-alanine is a precursor of carnosine Data are variable regarding endurance exercise. β-alanine with paresthesias at higher doses. Physicians who care for young athletes are encouraged to have an understanding of healthy and unhealthy weight-control methods; Health supervision visits for young athletes generally include history-taking to ascertain diet and physical activity patterns.
Acute weight loss through dehydration and the use of potentially harmful medications and supplements for weight control should be strongly discouraged; Physicians should counsel young athletes who express a desire to gain or lose weight to avoid weight-control methods that may have adverse health effects, such as acute weight loss through dehydration and the use of potentially harmful medications and supplements.
Many of these methods may have a negative effect on performance as well; Some states require a specific form for sports preparticipation examinations. Monitoring athletes with weight-control issues every 1 to 3 months can aid the physician in detecting excessive weight loss; There are no established recommendations for body fat percentages in adolescent athletes.
Rather than suggesting a specific percentage of body fat for an individual athlete, a range of values that is realistic and appropriate should be recommended; Physicians should counsel young athletes that weight gain or weight loss regimens should be initiated early enough to permit gradual weight change before a sport season.
Once the desired weight is obtained, the athlete should attempt to maintain a constant weight; and When opportunities for community education arise, pediatricians should collaborate with coaches and certified athletic trainers to encourage healthy eating and exercise habits.
AAP American Academy of Pediatrics. DXA dual-energy radiograph absorptiometry. LAW lowest allowable weight. NCAA National Collegiate Athletic Association. RDN registered dietitian nutritionist. FUNDING: No external funding. Prevalence of individual and combined components of the female athlete triad.
Disordered eating and menstrual irregularity in high school athletes in lean-build and nonlean-build sports. American College of Sports Medicine position stand.
Weight loss in wrestlers. Promotion of healthy weight-control practices in young athletes [published correction appears in Pediatrics. Effects of self-selected mass loss on performance and mood in collegiate wrestlers.
Onset of adolescent eating disorders: population based cohort study over 3 years. Identification and management of eating disorders in children and adolescents. Physiological consequences of hypohydration: exercise performance and thermoregulation.
Policy statement—climatic heat stress and exercising children and adolescents. Hypohydration during exercise in children: effect on thirst, drink preferences, and rehydration. Drink composition, voluntary drinking, and fluid balance in exercising, trained, heat-acclimatized boys.
Effect of drink flavor and NaCL on voluntary drinking and hydration in boys exercising in the heat. Exercise and fluid replacement. The effects of progressive dehydration on strength and power: is there a dose response?
Skeletal muscle strength and endurance are maintained during moderate dehydration. Active dehydration impairs upper and lower body anaerobic muscular power. Hydration and muscular performance: does fluid balance affect strength, power and high-intensity endurance?
Effect of body hypohydration on aerobic performance of boys who exercise in the heat. Two percent dehydration impairs and six percent carbohydrate drink improves boys basketball skills.
Hyperthermia and dehydration-related deaths associated with intentional rapid weight loss in three collegiate wrestlers—North Carolina, Wisconsin, and Michigan, November-December The National Collegiate Athletic Association Wrestling and Rules and Interpretations. The Wisconsin wrestling minimum weight project: a model for weight control among high school wrestlers.
NCAA rule change improves weight loss among national championship wrestlers. Wisconsin minimum weight program reduces weight-cutting practices of high school wrestlers. Blood and urinary measures of hydration status during progressive acute dehydration. Rehydration with drinks differing in sodium concentration and recovery from moderate exercise-induced hypohydration in man.
Rehydration after exercise with fresh young coconut water, carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage and plain water. Current status of body composition assessment in sport: review and position statement on behalf of the ad hoc research working group on body composition health and performance, under the auspices of the I.
Medical Commission. A quantitative critical review. Evaluation of the BOD POD and leg-to-leg bioelectrical impedance analysis for estimating percent body fat in National Collegiate Athletic Association Division III collegiate wrestlers.
Female athlete triad in elite swimmers of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Health and weight control management among wrestlers. A proposed program for high school athletes. The female athlete triad.
The IOC consensus statement: beyond the female athlete triad—Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport RED-S. Misunderstanding the female athlete triad: refuting the IOC consensus statement on Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport RED-S. Associations between disordered eating, menstrual dysfunction, and musculoskeletal injury among high school athletes.
Associations between the female athlete triad and injury among high school runners. Higher prevalence of eating disorders among adolescent elite athletes than controls.
Prevalence of eating disorders in elite athletes is higher than in the general population. Prevalence of disordered eating and pathogenic weight control behaviors among male collegiate athletes.
Risk and trigger factors for the development of eating disorders in female elite athletes. Long-term effect of weight loss on body composition and performance in elite athletes.
Recommendations for treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Position of the American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and athletic performance. Liver injury from herbals and dietary supplements in the U.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network. Self-perceived weight and anabolic steroid misuse among US adolescent boys. Misclassification of cardiometabolic health when using body mass index categories in NHANES Expected body weight in adolescents: comparison between weight-for-stature and BMI methods.
Carl, MD, MS, FAAP. Johnson, MD, FAAP. Martin, MD, FAAP. LaBella, MD, FAAP, Chairperson. Brooks, MD, FAAP.
Alex Diamond, DO, FAAP. William Hennrikus, MD, FAAP. Michele LaBotz, MD, FAAP. Kelsey Logan, MD, FAAP. Loud, MDCM, MSc, FAAP. Moffatt, MD, FAAP. Blaise Nemeth, MD, FAAP. Brooke Pengel, MD, FAAP. Andrew Peterson, MD, FAAP. Joel S.
Brenner, MD, MPH, FAAP. Amanda K. Weiss Kelly, MD, FAAP. Mark E.
Weight management for athletes maintenance is a balance Weight management for athletes the fro consumed Weight management for athletes Injury prevention through proper fueling the energy expended. For athletes to maintain their weight while manatement competitive, they must Weigut the energy athldtes. While our energy intake Wejght from the food and beverages that we consume, our total daily energy expenditure TDEE is generated from multiple components, including resting metabolic rate RMRthe thermic effect of food TEF and physical activity energy expenditure PAEE. PAEE is the energy expenditure above resting that results from skeletal muscle contraction, including the required movement, balance and maintenance of posture. Both ExEE and NEAT can impact the ability to maintain weight. It is also likely that the foods and drinks they consume will vary.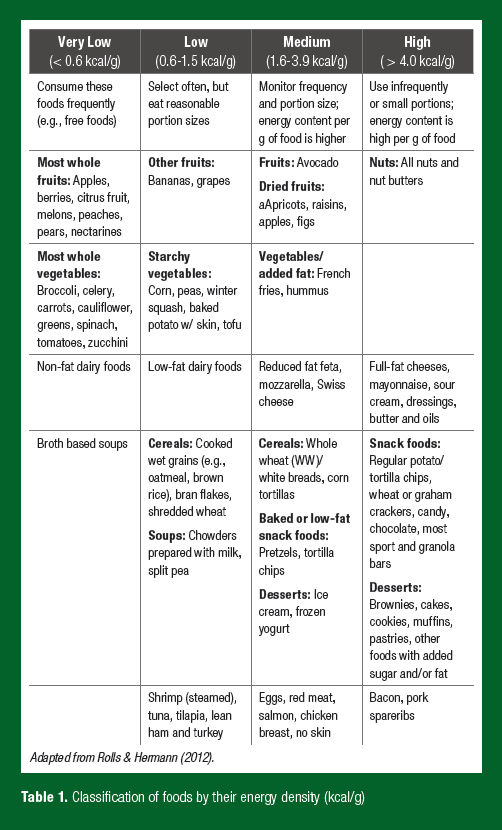
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht.
die Anmutige Mitteilung